
2004 Hayes St. Nashville TN, 37203 Suite 655
Tel: 615-866-9040
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
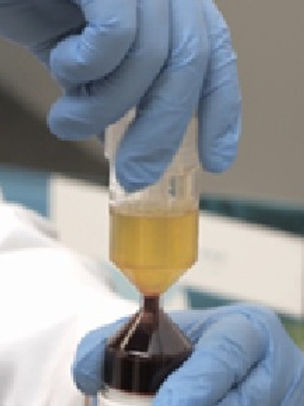
What is PRP?
Platelet-rich plasma consists of two elements: plasma, or the liquid portion of blood, and platelets, a type of blood cell that plays an important role in healing throughout the body. Platelets are well-known for their clotting abilities, but they also contain growth factors that can trigger cell reproduction and stimulate tissue regeneration or healing in the treated area. Platelet-rich plasma is simply blood that contains more platelets than normal.
Preparation: A sample of your blood is drawn, placed in a centrifuge to concentrate the platelets, and then injected into the target area
How PRP works?
Healing Boost: Platelets release growth factors that stimulate cell repair and regeneration.
Targeted Therapy: By injecting PRP into damaged tissues, the goal is to accelerate healing and reduce inflammation.
Common Uses
Tendon, Ligament, Muscle and Joint Injuries
PRP injections may be able to treat a range of musculoskeletal injuries and conditions. For example, chronic tendon injuries such as tennis elbow or jumper’s knee can often take a long time to heal, so adding PRP shots to a treatment regimen can help to stimulate the healing process, decrease pain and enable a return to activities sooner.
Post-surgical Healing
Clinicians first used PRP to accelerate healing after jaw or plastic surgeries. Now, post-surgical PRP injections have expanded to help heal muscles, tendons and ligaments, as procedures on these tissues have notoriously long recovery times.
Osteoarthritis
Early studies indicate that PRP injections may help treat osteoarthritis pain and stiffness by modulating the joint environment and reducing inflammation, but research is growing.